Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St.
Dorchester Center, MA 02124

My journey with you | All you wish will be here !!!

My journey with you | All you wish will be here !!!
Hash tables are a fundamental data structure in computer science, providing efficient data retrieval and storage. In this blog post, we will explore what hash tables are, their applications, how to implement them using Java’s HashMap, and tackle a classic example problem: the two-sum problem.
A hash table is a data structure that uses a hash function to map keys to values, allowing for fast data retrieval. The primary operations—insert, delete, and search—can typically be performed in constant time, O(1), under ideal circumstances.
Hash tables are widely used due to their efficiency and versatility. Some common applications include:
Java provides a built-in class called HashMap, which implements the hash table data structure. It allows for the storage of key-value pairs, where keys are unique.
Here’s a quick overview of how to use HashMap in Java:
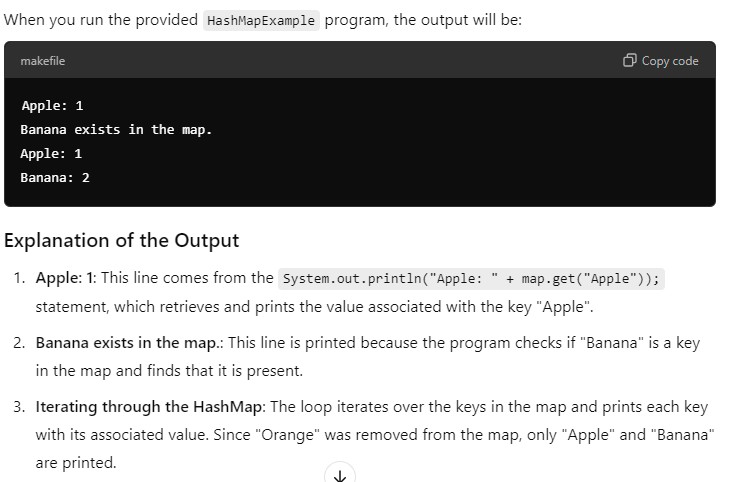
javaCopy codeimport java.util.HashMap;
public class HashMapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating a HashMap
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting values
map.put("Apple", 1);
map.put("Banana", 2);
map.put("Orange", 3);
// Retrieving values
System.out.println("Apple: " + map.get("Apple"));
// Checking existence
if (map.containsKey("Banana")) {
System.out.println("Banana exists in the map.");
}
// Removing values
map.remove("Orange");
// Iterating through the HashMap
for (String key : map.keySet()) {
System.out.println(key + ": " + map.get(key));
}
}
}
LinkedHashMap.The two-sum problem is a classic interview question: Given an array of integers and a target sum, find two numbers that add up to that sum. Using a hash table, we can solve this efficiently.
Given an array nums and an integer target, return the indices of the two numbers such that they add up to target.
javaCopy codeimport java.util.HashMap;
public class TwoSum {
public static int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int complement = target - nums[i];
if (map.containsKey(complement)) {
return new int[] { map.get(complement), i };
}
map.put(nums[i], i);
}
throw new IllegalArgumentException("No two sum solution");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {2, 7, 11, 15};
int target = 9;
int[] result = twoSum(nums, target);
System.out.println("Indices: " + result[0] + ", " + result[1]);
}
}

target - nums[i]).Hash tables are a powerful data structure that enables efficient data retrieval and manipulation. Java’s HashMap provides a straightforward way to implement this structure. By understanding hash tables and practicing problems like the two-sum problem, you can greatly enhance your programming skills.
ConcurrentHashMap for thread-safe operations.By mastering hash tables, you’ll be better equipped to handle various coding challenges and improve the performance of your applications. Happy coding!
Also see: The Z Blogs
my other Blog: The Z Blog ZB